
The Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent mainly took place between the 13th and the 18th centuries. Earlier Muslim conquests in the subcontinent include the invasions which started in the northwestern subcontinent (modern-day Pakistan), especially the Umayyad campaigns during the 8th century. Mahmud of Ghazni, Sultan of the Ghaznavid Empire, preserved an ideological link to the suzerainty of the Abbasid Caliphate and invaded vast parts of Punjab and Gujarat during the 11th century. After the capture of Lahore and the end of the Ghaznavids, the Ghurid ruler Muhammad of Ghor laid the foundation of Muslim rule in India in 1192. In 1202, Bakhtiyar Khalji led the Muslim conquest of Bengal, marking the easternmost expansion of Islam at the time.
The Ghurid Empire soon evolved into the Delhi Sultanate in 1206, ruled by Qutb ud-Din Aibak, the founder of the Mamluk dynasty. With the Delhi Sultanate established, Islam was spread across most parts of the Indian subcontinent. In the 14th century, the Khalji dynasty under Alauddin Khalji, extended Muslim rule southwards to Gujarat, Rajasthan, and the Deccan. The successor Tughlaq dynasty temporarily expanded its territorial reach to Tamil Nadu. The disintegration of the Delhi Sultanate, capped by Timur’s invasion in 1398, caused several Muslim sultanates and dynasties to emerge across the Indian subcontinent, such as the Gujarat Sultanate, Malwa Sultanate, Bahmani Sultanate, Jaunpur Sultanate, Madurai Sultanate, and the Bengal Sultanate. Some of these, however, were followed by Hindu reconquests and resistance from the native powers and states, such as the Telugu Nayakas, Vijayanagara, and Rajput states.
The Delhi Sultanate was replaced by the Mughal Empire in 1526, which was one of the three gunpowder empires. Emperor Akbar gradually enlarged the Mughal Empire to include a large portion of the subcontinent. Under Akbar, who stressed the importance of religious tolerance and winning over the goodwill of the subjects, a multicultural empire came into being with various non-Muslim subjects being actively integrated into the Mughal Empire’s bureaucracy and military machinery. The economic and territorial zenith of the Mughals was reached at the end of the 17th century, when under the reign of emperor Aurangzeb the empire witnessed the full establishment of Islamic Sharia through the Fatawa al-Alamgir.
The Mughals went into a sudden decline immediately after achieving their peak following the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, due to a lack of competent and effective rulers among Aurangzeb’s successors. Other factors included the expensive and bloody Mughal-Rajput Wars and the Mughal–Maratha Wars. The Afsharid ruler Nader Shah’s invasion in 1739 was an unexpected attack which demonstrated the weakness of the Mughal Empire. This provided opportunities for various regional states such as Rajput states, Mysore Kingdom, Nawabs of Bengal and Murshidabad, Maratha Empire, Sikh Empire, and Nizams of Hyderabad to declare their independence and exercising control over large regions of the Indian subcontinent further accelerating the geopolitical disintegration of the Indian subcontinent.
The founder of the empire, Cyrus the Great, launched the first of his two major invasions in 535 BCE, annexing the areas west of the Indus River that comprised the Achaemenid Empire’s eastern frontier.
After the death of Cyrus, Darius the Great I invaded Sindh and Punjab. In the list of Persian Invaders of India, the son of Darius is also included, who was embroiled in a war with the Greeks.
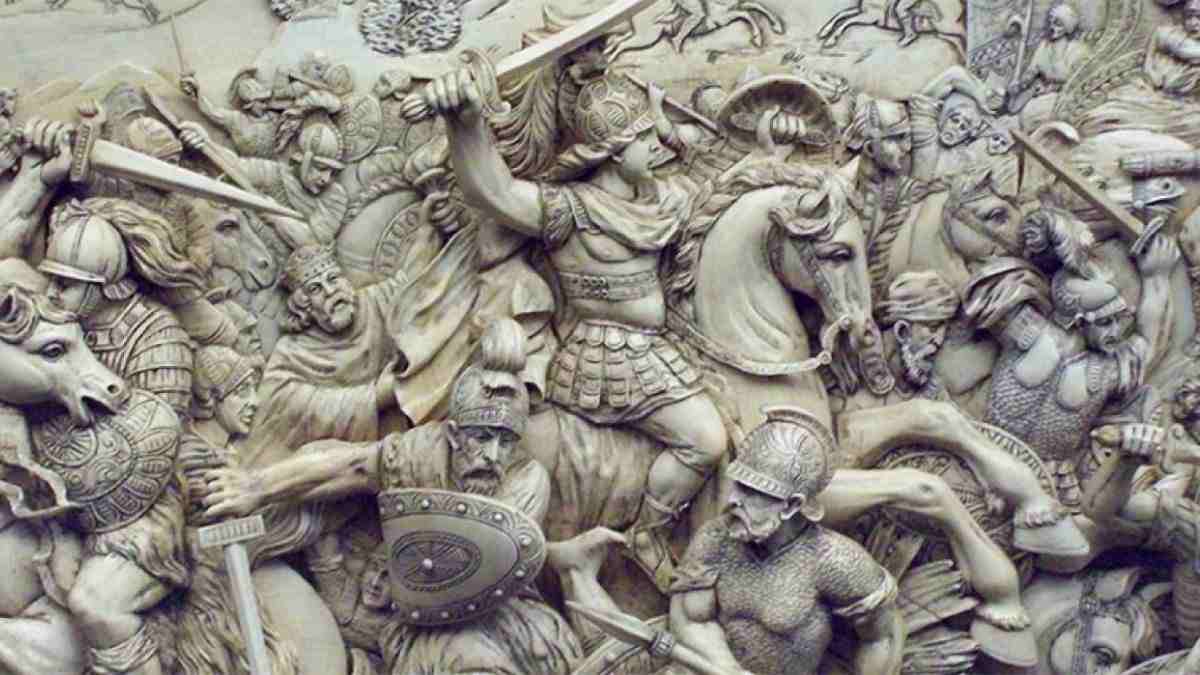
Alexander was one of the invaders of India in 327 BC. He divided his forces according to his plan, built a bridge over the Indus River, provisioned their men, and advanced to Taxila’s capital city.
Britishers were also Invaders of India, and their era is known as British India. They came to India on August 24, 1608, as merchants to lead the foreign invasion of India.


